Data Lake or Data Warehouse: what are the differences between these databases?

You may have noticed that data analysis has become an important tool for businesses, aiding in strategic management and generating new business opportunities. This is where the concepts of Data Lake and Data Warehouse come into play.
Both Data Lake and Data Warehouse are concepts related to Business Intelligence, or BI, which consists of the strategies and techniques used by companies to transform data into useful business information.
From the stages involved in data processing, Data Lakes and Data Warehouses function as repositories used to store, process, and protect information—whether structured or not—in large quantities.
However, despite their similarities, Data Lakes and Data Warehouses have distinct meanings and purposes. If you want to learn more about the differences between these terms, understand how they work, and how they are useful for different objectives, keep reading this article and deepen your knowledge!
What is a Data Lake?
As mentioned above, a Data Lake acts as a centralized repository for all types of data—raw, structured, semi-structured, and unstructured. In other words, it is a non-relational database used to store, process, and protect information collected on any scale.
Just as you can’t predict what you’ll find in a lake, the types of data found in a Data Lake are entirely unpredictable. This is because this type of database accepts all file and data formats without any logical connection between them, such as:
- Binary data: images, audio, and video
- Logs
- XML
- JSON
- CRMs
- ERPs
- Spreadsheets
- SQL
- Unstructured data: emails, documents
What is a Data Lake Used For?
One of the purposes of a Data Lake, precisely because it allows for the storage of disorganized information, is to serve as a source for Big Data and Business Intelligence strategies, enabling new intersections of distinct information—resulting in advanced analyses and new insights for businesses.
Additionally, it functions as a resource for centralizing all data from an organization in one place, allowing for the search, retrieval of relevant data, and structuring as it is used.
Other examples of Data Lake usage include: information base for Artificial Intelligence, data exploration, Machine Learning, and forecasting new trends.
What is a Data Warehouse?
A Data Warehouse is a data storage system that operates in an organized manner. In other words, it is a structured database, facilitating queries and analyses.
Aiming to answer specific and pre-defined questions, one of the principles of a Data Warehouse is to integrate information from different systems in periodic long-term updates, allowing for the visualization and control of reports.
Unlike a Data Lake, Data Warehouses store only structured data such as:
- CRMs
- ERPs
- Spreadsheets
- XLS
- SQL
What is a Data Warehouse Used For?
One of the main purposes of a Data Warehouse is to produce reports and historical analysis. With data produced from a reliable base, managerial decisions can be made with greater accuracy. This is because reports offer more grounding and precision.
It is worth noting that because organization is one of the main characteristics of a Data Warehouse, this storage mode offers greater agility in capturing and using data.
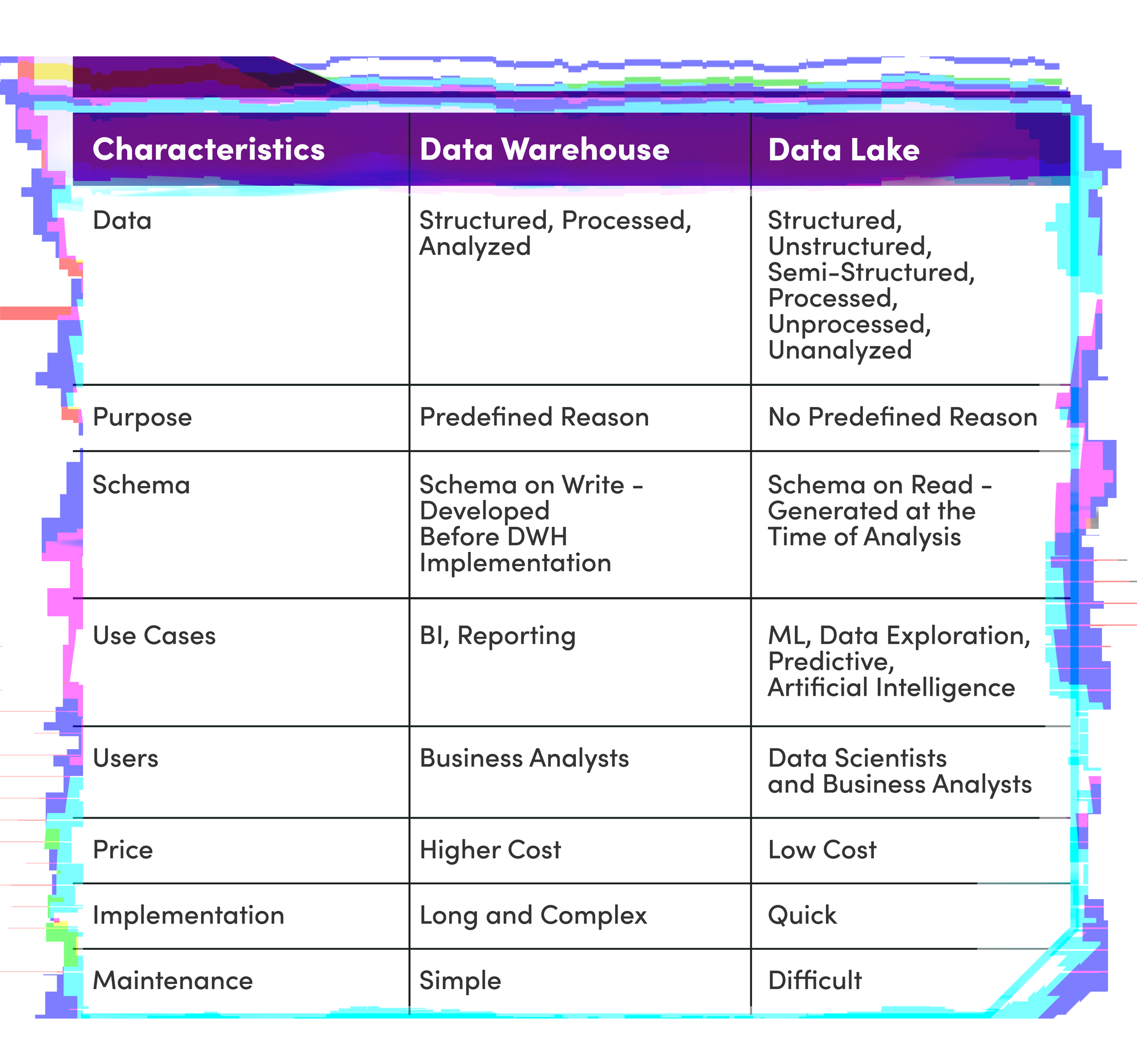
Data Lake vs Data Warehouse
As you may have noticed, Data Lakes and Data Warehouses have different dynamics. In other words, a Data Lake enables the creation of new connections between disorganized data, while a Data Warehouse allows for the construction of a periodic view through pre-programmed collected data.
Thus, both serve as tools for organizations seeking to better understand the market in which they operate through data science.
You can see the differences between these terms more clearly in the following sections:
Are Data Lakes and Data Warehouses Secure?
According to privacy policies, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Brazilian General Data Protection Law (LGPD), both Data Lakes and Data Warehouses are useful tools for improving data management within companies and, consequently, strengthening the protection and security of information.
Additionally, in these databases, it is possible to establish security rules, ensure data quality, and maintain active control over the lifecycle of processed information.
Did you find this content useful? You can access more articles like this on the BugHunt Blog!

